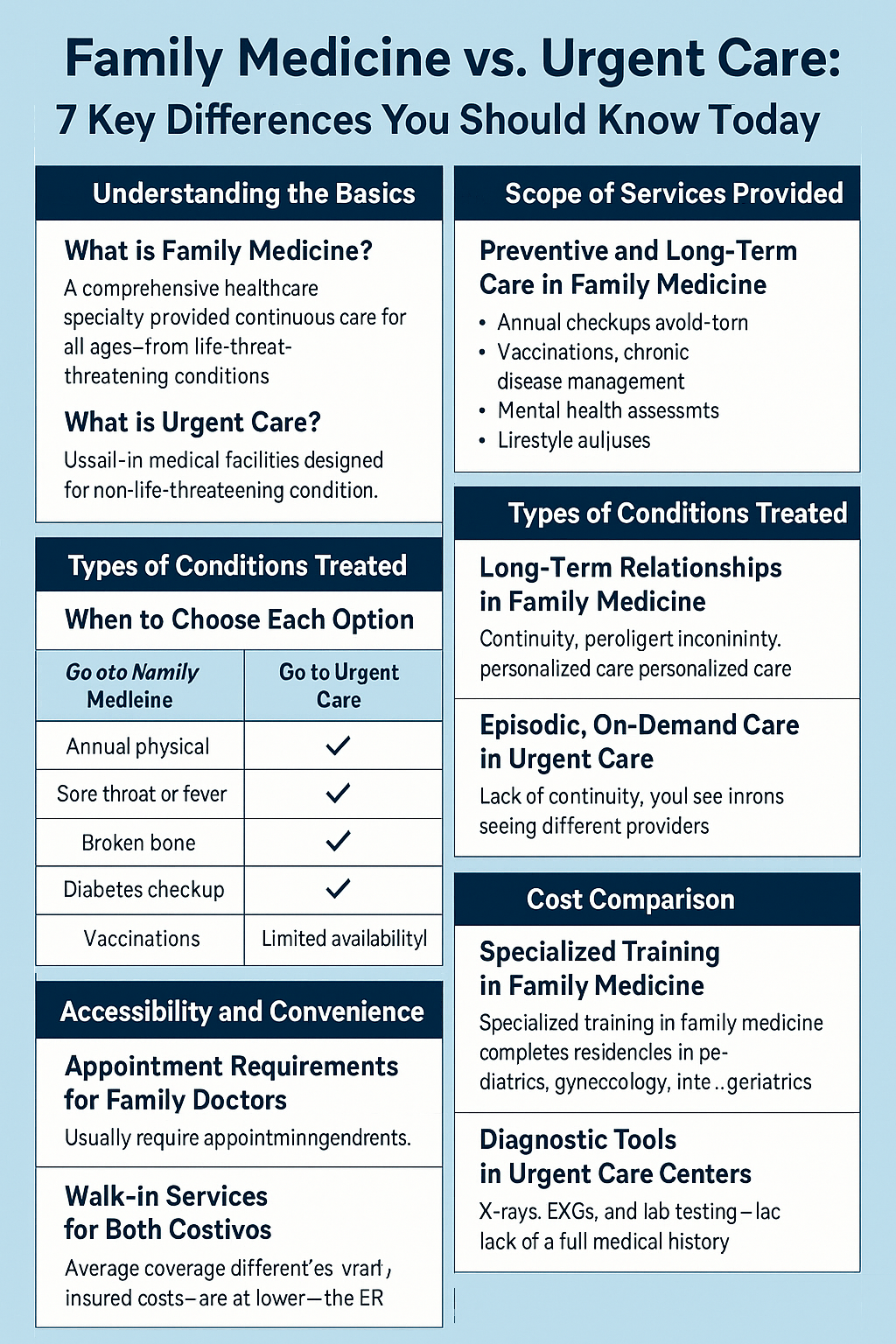
What is Family Medicine?
Family medicine is a comprehensive healthcare specialty that offers continuous care for individuals of all ages—from newborns to the elderly. A family doctor, also known as a primary care physician (PCP), builds a long-term relationship with patients, focusing on preventive care, chronic disease management, and holistic health.
What is Urgent Care?
Urgent care centers are walk-in medical facilities designed to treat acute, non-life-threatening conditions such as infections, minor injuries, and allergic reactions. They bridge the gap between primary care and emergency rooms, offering convenient and immediate access when your doctor’s office is closed or unavailable.
Scope of Services Provided
Preventive and Long-Term Care in Family Medicine
Family doctors don’t just treat illnesses—they work to prevent them. Services often include:
-
Annual checkups and wellness exams
-
Vaccinations and immunizations
-
Chronic disease management (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
-
Mental health assessments
-
Lifestyle and nutrition counseling
Immediate and Acute Care in Urgent Care Centers
Urgent care clinics are best for one-time, immediate needs such as:
-
Cold, flu, and COVID-19 symptoms
-
Cuts needing stitches
-
Sprains or minor fractures
-
Skin rashes or infections
-
Minor burns or allergic reactions
They generally don’t offer follow-up or preventive care services.
Types of Conditions Treated
Chronic Illness Management vs. Acute Illness Treatment
Family medicine specializes in the ongoing care of chronic conditions like asthma, arthritis, and diabetes. Urgent care, by contrast, treats short-term issues that need quick attention but are not severe enough for the ER.
When to Choose Each Option
| Condition | Go to Family Medicine | Go to Urgent Care |
|---|---|---|
| Annual physical | ✅ | ❌ |
| Sore throat or fever | ✅ (if during office hours) | ✅ |
| Broken bone | ❌ | ✅ |
| Diabetes checkup | ✅ | ❌ |
| Vaccinations | ✅ | ✅ (limited availability) |
Continuity of Care and Patient Relationship
Long-Term Relationships in Family Medicine
A key strength of family medicine is continuity. Doctors keep a detailed record of your health history, allowing for consistent, personalized care and early detection of issues.
Episodic, On-Demand Care in Urgent Care
Urgent care lacks continuity. While convenient, you’ll likely see different providers each time, and follow-ups are rarely part of the service.
Accessibility and Convenience
Appointment Requirements for Family Doctors
You usually need an appointment to see your family doctor, which can sometimes take days or weeks to schedule.
Walk-In Services in Urgent Care Clinics
Urgent care centers typically allow walk-ins and have shorter wait times, making them ideal for unexpected issues that can't wait.
Hours of Operation and Availability
Standard Office Hours of Family Practices
Family medicine clinics usually operate during traditional business hours: Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 5 p.m., with limited or no weekend availability.
Extended and Weekend Hours of Urgent Care
Urgent care is designed for accessibility, often staying open late, on weekends, and even holidays—perfect for after-hours medical needs.
Cost Comparison
Insurance Coverage Differences
Both services are usually covered by insurance, but co-pays and out-of-pocket costs vary. Urgent care tends to cost more than a standard PCP visit but less than an emergency room trip.
Average Visit Costs for Both Services
| Type of Care | Average Cost (With Insurance) | Average Cost (Without Insurance) |
|---|---|---|
| Family Medicine | $100–$150 | $150–$200 |
| Urgent Care | $150–$250 | $200–$300 |
Level of Medical Expertise and Equipment
Specialized Training in Family Medicine
Family doctors complete extensive training, including residencies in various fields such as pediatrics, gynecology, internal medicine, and geriatrics.
Diagnostic Tools in Urgent Care Centers
Urgent care centers are equipped with basic diagnostic tools like X-rays, EKGs, and lab testing, but they lack the depth and continuity of a full medical history.
Pediatric and Geriatric Considerations
Family Medicine for All Ages
Family physicians are trained to care for patients across the lifespan. They monitor developmental milestones for children and manage age-related issues in seniors.
Urgent Care and Age-Specific Services
While urgent care can treat children and elderly patients, they may not have specialized staff or pediatric/geriatric expertise.
Referral Needs and Specialist Access
Coordinated Referrals by Family Physicians
Family doctors can refer you to specialists and collaborate with them on your care, ensuring a streamlined process.
Limited Referral Capabilities of Urgent Care
Urgent care can suggest seeing a specialist but typically does not coordinate ongoing care or make formal referrals.
Geographic Availability
Family Clinics vs. Ubiquity of Urgent Care
Family medicine practices may be less numerous in rural areas. Urgent care centers, especially chains, are often more widespread and accessible.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction
Personalized vs. Quick Service
Family medicine focuses on personalization and trust. Urgent care offers quick resolutions but may lack a personal touch.
Impact on Public Health and Community
Family Medicine’s Role in Community Wellness
Family doctors play a critical role in early intervention, disease prevention, and health education in communities.
Urgent Care's Role in Decongesting ERs
Urgent care facilities help alleviate the burden on emergency departments, ensuring critical care is reserved for life-threatening situations.
Ideal Scenarios to Choose Each One
When You Should Visit Family Medicine
-
Ongoing health concerns
-
Routine checkups
-
Preventive screenings
-
Managing multiple prescriptions
When Urgent Care is the Right Choice
-
You’re sick and can’t wait for a doctor’s appointment
-
You need care outside office hours
-
You have a minor injury or illness requiring quick attention
Expert Opinions and Real-Life Testimonials
Physician Insights
“Family medicine allows us to treat the whole person—not just symptoms. We build relationships that last a lifetime.” – Dr. Amy Watson, MD
Patient Stories
“Urgent care helped me when I had a terrible sinus infection on a Sunday. But for everything else, I stick with my family doctor.” – Jennifer R., 42
F.A.Q.
Think about urgency, convenience, your health history, and whether you need follow-up or specialized care.
Absolutely. In fact, family doctors often manage complex medication regimens over time.
Yes. Out-of-pocket costs can be high, especially for procedures and lab tests.
Urgent care doctors are licensed and capable but may not have specialized training in long-term patient care like family physicians do.
Usually not. Most urgent care visits are one-off, and you’ll need to share your medical background each time.
Yes, for non-emergency issues that need immediate attention. But family doctors offer better long-term care.
Making the Right Healthcare Decision for You
Choosing between family medicine vs. urgent care doesn’t have to be complicated. For long-term, personalized, and preventive healthcare, family medicine is the gold standard. For sudden illnesses or injuries when time is of the essence, urgent care is your go-to solution. Understanding the strengths of each helps you stay healthy, save time, and make empowered decisions for yourself and your family.
The Crucial Role of Nutrition in Preventing Chronic Diseases
Jimenez2024-11-16T22:59:09+00:00May 7, 2024|Categories: Nutrition, Prevention|
The Crucial Role of Nutrition in Preventing Chronic Diseases As a medical doctors, we often emphasize to [...]
The Impact of Loneliness and Social Isolation on Older Adults
Jimenez2024-11-16T23:00:41+00:00March 6, 2024|Categories: elderly, Mental Disease|
Loneliness and social isolation are distinct yet interrelated concepts that significantly impact the well-being [...]





